LevelDB 源码分析(四) - Compaction 文件选择
背景
leveldb 是一个写效率十分高的存储引擎, 一次写操作只需要顺序写日志(WAL),内存跳表插入(logn)
但是如此以来读性能就有所下降,在最差的情况下可能需要查找以下所有文件
1 | MemTable --> Immutable MemTable --> Level 0 files --> Level 1 files -->Level 2 files ......-->Level 6 files |
所以引入 Compaction 可以带来如下好处
- 平衡读写差异,将相关文件进行合并
- 删除过时数据,减少数据量
分析
Compaction 是通过后台线程调用 BackgroundCompaction 来触发,上一章中我们分析了如何触发 Compaction 并分析了当中的 Minor Compaction ,本文将关注当中的 Major Compaction (SSTable 当中的 Compaction)
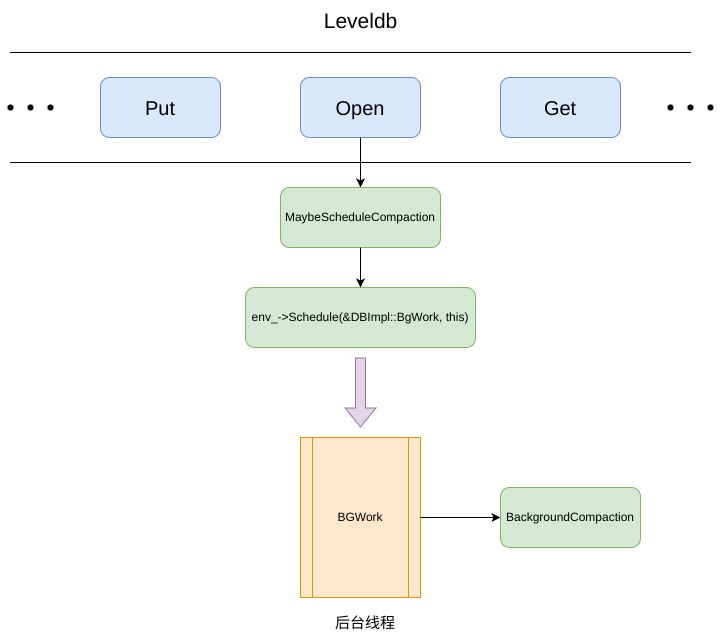
BackgroundCompaction 主要有两个部分组成
Minor Compaction
1 | if (imm_ != nullptr) { |
用来检测当前是否存在 Immutable ,如果存在则将该 Immutable -> SSTable
Manual Compaction
顾名思义 Manual Compaction,即为手动压缩
1 | bool is_manual = (manual_compaction_ != nullptr); |
is_manual 是一个 bool 值,通过该值来判断是否执行 Manual Compaction, 而该值是通过 manual_compaction_ 是否为 nullptr 来确定,而 manual_compaction_ 是在 leveldb 对外接口 CompactRange 中设置,相当是对外提供手动 Compaction 的接口
Major Compaction
Major Compaction 核心便是在 level 和 level + 1 层中进行 Compaction 操作,所以第一步便是需要确定参与 Compaction 的 level 层级以及文件,而这便是由 PickCompaction 决定
1 | c = versions_->PickCompaction(); |
Compaction 文件的选择
level(n)的文件选择
并不是每一次调用 PickCompaction 都可以找出 level 层级与文件,这取决于两个因素
- current_->compaction_score_ >= 1 : 一个 level 层级的文件太多,需要 Compaction 到 level + 1 层
- current_->file_to_compact_ != nullptr : 一个文件 seek 的次数太多,优化读性能,进行 Compaction
由文件 seek 过多引发的 Compaction
1 | const bool seek_compaction = (current_->file_to_compact_ != nullptr); |
当一个文件 seek 过多时,会在当前版本中记录它的层级与文件元数据 FileMetaDate,并将其写入到 inputs_[0] 中
1 | inputs_ 的类型是 std::vector<leveldb::FileMetaData *> leveldb::Compaction::inputs_[2] |
由文件数量引发的 Compaction
1 | const bool size_compaction = (current_->compaction_score_ >= 1); |
当某一个层级的文件数量过多时,当前版本会记录需要 Compaction 的层级。
1 | leveldb 会为每一层进行打分,如果该层的分数大于等于 1,则标记为需要 Compaction, |
之后从该层中选出一个文件插入 inputs_[0] 中,如果没有符合要求的而插入 当前版本 level 层中的第一个文件
这里的 compact_pointer_[level] 是是什么含义?
1 | compact_pointer_ 的定义为 std::string compact_pointer_[7] |
在之后的代码分析中会涉及到
但是由于 level 0 层中的文件并不是有序的,且存在文件间重叠的现象,所以需要将该层中所有文件插入到 inputs_[0] 中进行后续处理
1 | // Files in level 0 may overlap each other, so pick up all overlapping ones |
level(n + 1)的文件选择
level n+1 层文件的选择位于 SetupOtherInputs
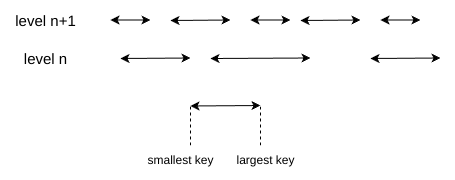
为了方便表示,每一个文件用横线表示,横线的长度代表 key 的范围,所以 level 层的文件 key 范围比 level + 1 层的 key 范围 大,但是 level + 1 层的文件个数相比而言就会多些
在选择 level n+1 层之前,leveldb做了一个优化,将临近的文件也加入到 Compaction 集合中
1 | const int level = c->level(); |
如下图所示
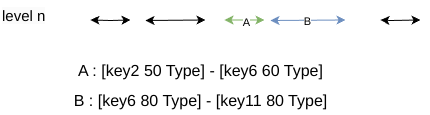
A 中的 largets key 与 B 中的 smallest key
- user key 相同,都是 key6
- B 的 SequenceNumber 比 A 中的大
对于这种情况,一般来说 key 是连续的,所以将该文件也加入到 Compaction 中,可以避免相同的 Key 分布在两个层级中,减少查找的开销同时避免多次 Compaction
之后添加 level n+1 层的文件
1 | // 根据 level 层文件的范围添加 level + 1 层 |
同样也对 level + 1 层进行了添加临近文件的优化,之后联合这两个层级计算key的范围
原本这样就完成了对 level 与 level + 1 层的文件选择,但是 leveldb 还添加了一个优化:在不影响 level + 1 层文件下尽可能的增加 level 层需要 Compaction 的文件,同时增加的文件不能超出本层的文件大小限制
如下图所示:
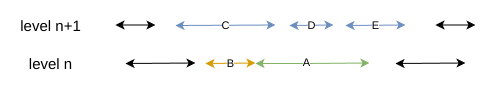
A 是 level 层被选出需要 Compaction 的文件,根据其范围可以在 level n + 1 层中找出对应的 C、D、E, 所以此时可以增加 B 文件,因为 B 文件的引入并不会引起 level n + 1 层文件的变化
现在分析如下图:
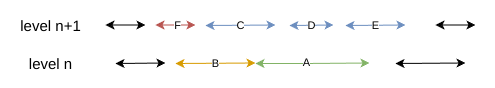
如果引入 B,则 Compaction 到 level + 1 的文件会与 F 发生重叠,因为当前 B 中的文件已经与 F 有重叠部分,这样就打破了 level 1 ~ level 6 之间不能相互重叠的限制
1 | // See if we can grow the number of inputs in "level" without |
之后通过这两层文件的 smallest key 与 largest key 计算与其祖父母的重叠文件(level + 2 层文件)
1 | // Compute the set of grandparent files that overlap this compaction |
计算 compact_pointer_
1 | // Update the place where we will do the next compaction for this level. |
还记得前面说过 compact_pointer_[level] 记录了上一次 PickCompaction 中 level 层的最大 key ,方便下一次 PickCompaction 的调用。
至此,Compaction 的文件选择就结束了,有关 Compaction 具体的执行过程我们在下一章节中再分析分析




